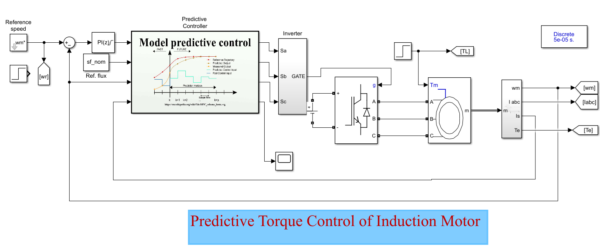
Predictive Torque Control of Induction Machines Based on State-Space Models
- Objective: To improve control accuracy, enhance dynamic response, and reduce torque/flux ripples in AC drives by incorporating a more accurate system model into the control algorithm.
- State-Space Model: Unlike simple Euler approximations, this method uses a discrete-time state-space model that accurately represents the induction machine, including the time-varying rotor speed term.
- Methodology:
- Modeling: A discrete-time model of the induction machine is updated at every sampling instant.
- Prediction: The algorithm predicts future stator current and flux values for each of the eight possible voltage vectors generated by a two-level inverter.
- Cost Function Optimization: A cost function, which often includes torque error, flux magnitude error, and sometimes switching frequency constraints, is evaluated for each prediction.
- Selection: The voltage vector that minimizes the cost function is selected for the next sampling interval.
- Key Features:
- Flexibility: The structure allows for the easy inclusion of system non-linearities, constraints, and operational limitations (e.g., overcurrent protection).
- Fast Response: Provides superior dynamic response compared to traditional DTC
Reference paper:
Miranda, H., Cortés, P., Yuz, J.I. and Rodríguez, J., 2009. Predictive torque control of induction machines based on state-space models. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 56(6), pp.1916-1924.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.